Hello everyone hope everyone is doing well. My name is Surya L, the purpose of this blog is to teach all about JavaScript Operators.
Contents:
- Arithmetic Operations In JavaScript
- Increment and Decrement Operation in JavaScript
- Compound Assignment with Arithmetic Operations
- Comparison Operator
- JavaScript Bitwise Operators
Arithmetic Operations In JavaScript
Add Two Numbers with JavaScript:
JavaScript uses the + symbol as an addition operator when placed between two numbers.
Example:
const myVar = 5 + 10;//Adds 5+10 =15
const sum = 10 + 10;//Adds 10+10 =20
Subtract One Number from Another with JavaScript:
JavaScript uses the - symbol for subtraction.
Example:
const myVar = 12 - 6;//Subtract 12-6=6
const difference = 45 - 33;//Subtract 45-33=12
Multiply Two Numbers with JavaScript
JavaScript uses the * symbol for multiplication of two numbers.
Example
const myVar = 13 * 13;
//myVar would have the value 169.
const product = 8 * 10;//8*10=80
Divide One Number by Another with JavaScript
JavaScript uses the / symbol for division.
Example
const myVar = 16 / 2;//myVar now has the value 8.
const quotient = 66 / 33; //66 divided by 22 = 2
Finding a Remainder in JavaScript
The remainder operator % gives the remainder of the division of two numbers. Example
5 % 2 = 1 ;
17 % 2 = 1;//(17 is Odd)
48 % 2 = 0;//(48 is Even)
Increment and Decrement Operation in JavaScript
Increment(++) and Decrement Operation(--) in JavaScript.
Increment a Number with JavaScript
You can easily increment or add one to a variable with the ++ operator. For example
i++;
//is the equivalent of
i = i + 1;
//Note: The entire line becomes i++;, eliminating the need for the equal sign.
let myVar = 87;
myVar++;//You can easily increment or add one to a variable with the ++ operator.
Decrement a Number with JavaScript
You can easily Decrement or Subtract one to a variable with the -- operator. For example
i--;
//is the equivalent of
i = i -1;
//Note: The entire line becomes i--;, eliminating the need for the equal sign.
let myVar = 11;
myVar--;//You can decrement or decrease a value of myVar by one with the -- operator.
Compound Assignment with Arithmetic Operations
1.Compound Assignment With Augmented Addition:
Assignments are commonly used to modify the contents of a variable in programming. All things to the right of the equals sign are evaluated first, so we can say
myVar = myVar + 5;
//to add 5 to myVar. Since this is such a common pattern, there are operators which do both a mathematical operation and assignment in one step.
//One such operator is the += operator.
let myVar = 1;
myVar += 5;
console.log(myVar);
2.Compound Assignment With Augmented Subtraction
Like the += operator above, we can use -= subtracts a number from a variable.
myVar = myVar - 5;
//will subtract 5 from myVar. This can be rewritten as:
myVar -= 5;
3.Compound Assignment With Augmented Multiplication
The *= operator multiplies a variable by a number.
myVar = myVar * 5;
//will multiply myVar by 5. This can be rewritten as:
myVar *= 5;
4.Compound Assignment With Augmented Division
The /= operator divides a variable by another number.
myVar = myVar / 5;
Will divide myVar by 5. This can be rewritten as:
myVar /= 5;
Boolean Values
Booleans can only be one of two values: true or false. They are basically little on-off switches, where true is on and false is off. These two states are mutually exclusive.
Comparison Operator
Equality Operator(==)
There are many comparison operators in JavaScript. All of these operators return a Boolean true or false value.
The most basic operator is the equality operator ==. The equality operator compares two values and returns true if they're equivalent or false if they are not.
function testEqual(val) {
if (val==12) { // If this condition is true
return "Equal";//This line is executed
}
return "Not Equal";//Or This line is executed
}
testEqual(10);
Strict Equality Operator
The equivalent of the equality operator (==) is strict equality (===). The strict equality operator, however, does not convert the values being compared to a common type, unlike the equality operator.
As long as the values being compared have different types, the strict equality operator returns false.
Examples
3 === 3 // true
3 === '3' // false
Inequality Operator
An inequality operator (!=) is the opposite of an equality operator. If not equal, it returns false, whereas if equal, it returns true. As with equality, the inequality operator converts the data types of values during comparison.
function testNotEqual(val) {
if (val!=99) {//IF val is not equal to 99
return "Not Equal";//this line is executed
}
return "Equal";
}
testNotEqual(10);
Strict Inequality Operator
The strict inequality operator (!==) is the logical opposite of the strict equality operator. It means "Strictly Not Equal" and returns false where strict equality would return true and vice versa. The strict inequality operator will not convert data types.
function testStrictNotEqual(val) {
if (val!==17) {//IF val is not equal to 99 and the data type should match
return "Not Equal";
}
return "Equal";
}
testStrictNotEqual(10);
Greater Than Operator
The greater than operator (>) compares the values of two numbers. If the number to the left is greater than the number to the right, it returns true. Otherwise, it returns false.
function testGreaterThan(val) {
if (val>100) { //IF val is greater then 100
return "Over 100";//this line is executed
}
if (val>10) {
return "Over 10";
}
return "10 or Under";
}
testGreaterThan(10);
Greater Than Or Equal To Operator
The greater than or equal to operator (>=) compares the values of two numbers. If the number to the left is greater than or equal to the number to the right, it returns true. Otherwise, it returns false.
function testGreaterOrEqual(val) {
if (val>=20) { //IF val is greater Or Equal To 20
return "20 or Over";//this line is executed
}
if (val>=10) {
return "10 or Over";
}
return "Less than 10";
}
testGreaterOrEqual(10);
Less Than Operator
The less than operator (<) compares the values of two numbers. If the number to the left is less than the number to the right, it returns true. Otherwise, it returns false. Like the equality operator, the less than operator converts data types while comparing.
function testLessThan(val) {
if (val<25) {
return "Under 25";
}
if (val<55) {
return "Under 55";
}
return "55 or Over";
}
testLessThan(10);
Less Than Or Equal To Operator
The less than or equal to operator (<=) compares the values of two numbers. If the number to the left is less than or equal to the number to the right, it returns true. If the number on the left is greater than the number on the right, it returns false. Like the equality operator, the less than or equal to operator converts data types.
function testLessOrEqual(val) {
if (val<=12) {//IF val is less Or Equal To 12
return "Smaller Than or Equal to 12";//this line is executed
}
if (val<=24) {
return "Smaller Than or Equal to 24";
}
return "More Than 24";
}
testLessOrEqual(10);
JavaScript Bitwise Operators
Bitwise AND Operator(&)
Sets each bit to 1 if both bits are 1
(13==20 & 25==33) = false
(11==11 & 25==25)=true

Bitwise OR Operator(|)
Sets each bit to 1 if one of two bits is 1
(13==20 |25==33) = false
(11==11 |25==28)=true
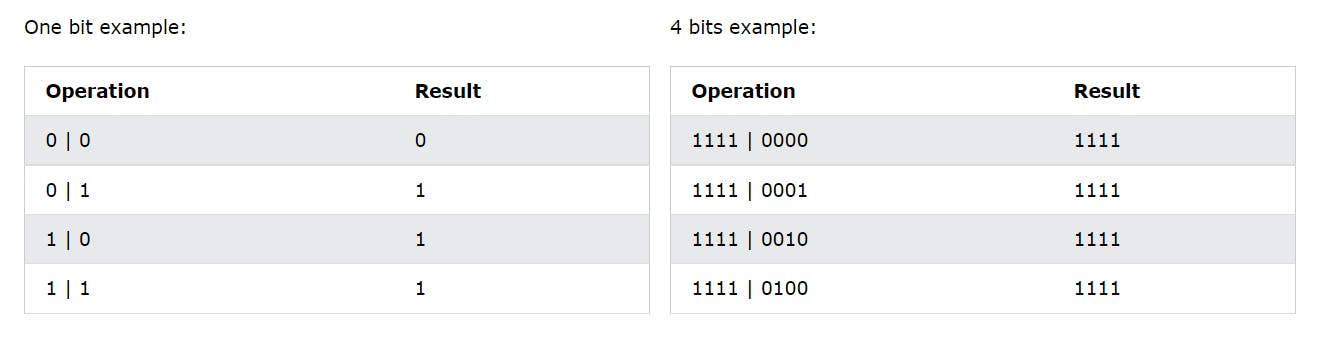
Bitwise XOR(^) Operator
Sets each bit to 1 if only one of two bits is 1
(10==20 ^ 20==33) = false
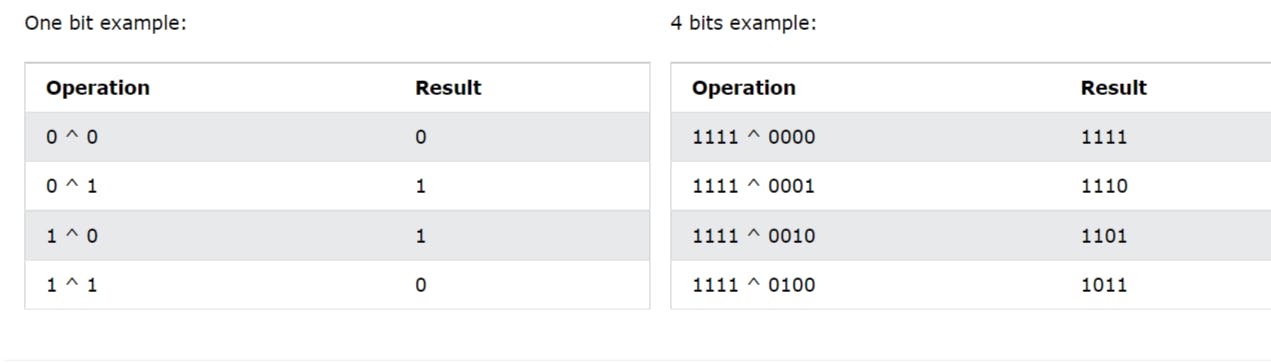
NOT(~) Operator
Inverts all the bits For Example:
0 to 1
1 to 0
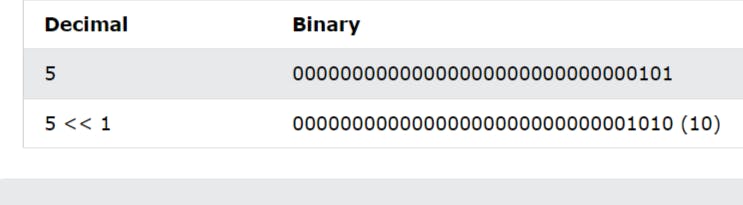
Bitwise Left Shift(<<)
Shifts left by pushing zeros in from the right and let the leftmost bits fall off
(10<<2) = 40
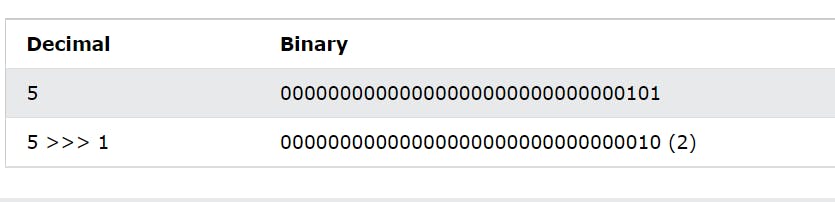
(>>) Signed right shift
Shifts right by pushing copies of the leftmost bit in from the left, and let the rightmost bits fall off
(10>>2) = 2

Zero fill right shift(>>>)
Shifts right by pushing zeros in from the left, and let the rightmost bits fall off
(10>>>2) = 2
Credits: I learned this topics in FreeCodeCamp ,W3School & JavaTpoint which I explained in minified version
Thanks for reading the blog. Do let me know what you think about it.

