How to use Array? And Array Functions in JavaScript
In a Simplified Manner with examples about Array and its functions
Table of contents
- Content of the Blog
- Store Multiple Values in one Variable using JavaScript Arrays
- Nest one Array within Another Array
- Access Array Data with Indexes
- Modify Array Data With Indexes
- Access Multi-Dimensional Arrays With Indexes
- Manipulate Arrays With push()
- Manipulate Arrays With pop()
- Manipulate Arrays With shift()
- Manipulate Arrays With unshift()
- A Simple Program
Hello everyone hope everyone is doing well. My name is Surya L, the purpose of this blog is to teach all about JavaScript Array and its Functions.
Content of the Blog
- What is an Array?
- Store Multiple Values in one Variable using JavaScript Arrays
- Nest one Array within Another Array
- Access Array Data with Indexes
- Modify Array Data With Indexes
- Access Multi-Dimensional Arrays With Indexes
- Manipulate Arrays With push()
- Manipulate Arrays With pop()
- Manipulate Arrays With shift()
- Manipulate Arrays With unshift()
What is an Array?
In computing, the term array refers to a collection of items stored on contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. An array's index starts at 0 and is called Zero indexing.
Store Multiple Values in one Variable using JavaScript Arrays
Using JavaScript array variables, we can store several pieces of data in one place.
Array declarations start with an opening square bracket, end with a closing square bracket, and each entry is separated by a comma, as shown below:
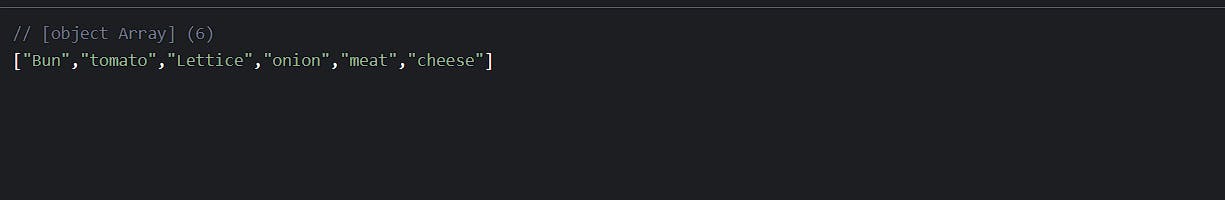
const burger = ["Bun", "tomato", "Lettice", "onion", "meat" , "cheese"];
console.log(burger);
The output of the above code 👇
Nest one Array within Another Array
Arrays can also be nested within arrays, as shown below:
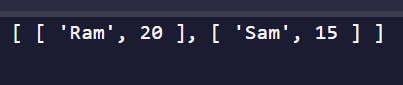
const teams = [["Sam", 23], ["Ram", 45]];
console.log(teams);
The output of the above code 👇
Access Array Data with Indexes
We can access the data inside arrays using indexes.
Array indexes are written in the same bracket notation that strings use, except that instead of specifying a character, they are specifying an entry in the array. Like strings, arrays use zero-based indexing, so the first element in an array has an index of 0.
Example
const myArray = [50, 60, 70];
var myData=myArray[0];//assigns 50 which is at 0 index of myArray variable to myData
console.log(myArray[0]);
Modify Array Data With Indexes
The entries of arrays are mutable and can be changed freely, even if the array was declared with const.
Example
const myArray = [18, 64, 99];
myArray[0]=45;//This changes the first value of myArray Variable with 45
console.log(myArray);
The output of the above code 👇
[ 45, 64, 99 ]
Access Multi-Dimensional Arrays With Indexes
The most effective way to think of a multi-dimensional array is as an array of arrays. When you use brackets to access your array, the first set of brackets refers to the outermost (first-level) entries, and each additional pair refers to the subsequently deeper levels. For example:
const myArray = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
[[10, 11, 12], 13, 14],
];
const myData = myArray[2][1];
console.log(myData);
The output of the above code 👇
8
Manipulate Arrays With push()
An easy way to append data to the end of an array is via the push() function. .push() takes one or more parameters and "pushes" them onto the end of the array.
Examples:
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
arr1.push(4);
const arr2 = ["Stimpson", "J", "cat"];
arr2.push(["happy", "joy"]);
console.log(arr1);
console.log(arr2);
The output of the above code 👇
[ 1, 2, 3, 4 ] [ 'Stimpson', 'J', 'cat', [ 'happy', 'joy' ] ]
Manipulate Arrays With pop()
The pop() function is an easy way to remove data to an array.
The .pop() function takes one or more parameters and removes from the end of the array.
For example:
const myArray = [["John", 23], ["cat", 2]];
var removedFromMyArray=myArray.pop();
//This line of code remove the last array in the myArray variable ["cat", 2] and assigns it to removedFromMyArray variable
console.log(removedFromMyArray);
The output of the above code 👇
[ 'cat', 2 ]
Manipulate Arrays With shift()
The pop() function removes the last element of an array. What if you want to remove the first?
This is where .shift() comes in. It works the same as .pop(), except that it removes the first element instead of the last. For example:
const myArray = [["John", 23], ["dog", 3]];
var removedFromMyArray=myArray.shift();
var removedFromMyArray=myArray.shift(); This function is same as pop function, the only differnce is it removes the first value of myArray variable and store it to removedFromMyArray variable.
The output of the above code 👇
[ 'John', 23 ]
Manipulate Arrays With unshift()
Not only can you shift elements off the beginning of an array, you can also unshift elements to the beginning of an array i.e. add elements in front of the array.
.unshift() works exactly like .push(), but instead of adding the element at the end of the array, unshift() adds the element at the beginning of the array.
For example:
const myArray = [["John", 23], ["dog", 3]];
myArray.shift();
console.log(myArray.unshift(["Paul", 35]));
myArray.unshift(["Paul", 35]); This line Adds ["Paul", 35]to the first position of myArray variable
A Simple Program
An Simple Shopping list array
const myList = [["Chocolate Bar", 15],["Ice Cream", 5],["Beer", 1],["Mask", 15],["Phone", 8]];//This assigns 5 sub-arrays in the list
console.log(myList);
The output of the above code 👇
[ [ 'Chocolate Bar', 15 ], [ 'Ice Cream', 5 ], [ 'Beer', 1 ], [ 'Mask', 15 ], [ 'Phone', 8 ] ]
Credits: I learned this topics in FreeCodeCamp which I explained in minified version
Thanks for reading the blog. Do let me know what you think about it.

